Creating an OPNsense virtual machine
Let’s take a look at an illustrative example of setting up a virtual machine with OPNsense in the Yandex Cloud infrastructure.
- First of all, it is necessary to create a virtual machine. The deployment process will be considered through the Yandex Cloud web interface (see Figure 1).
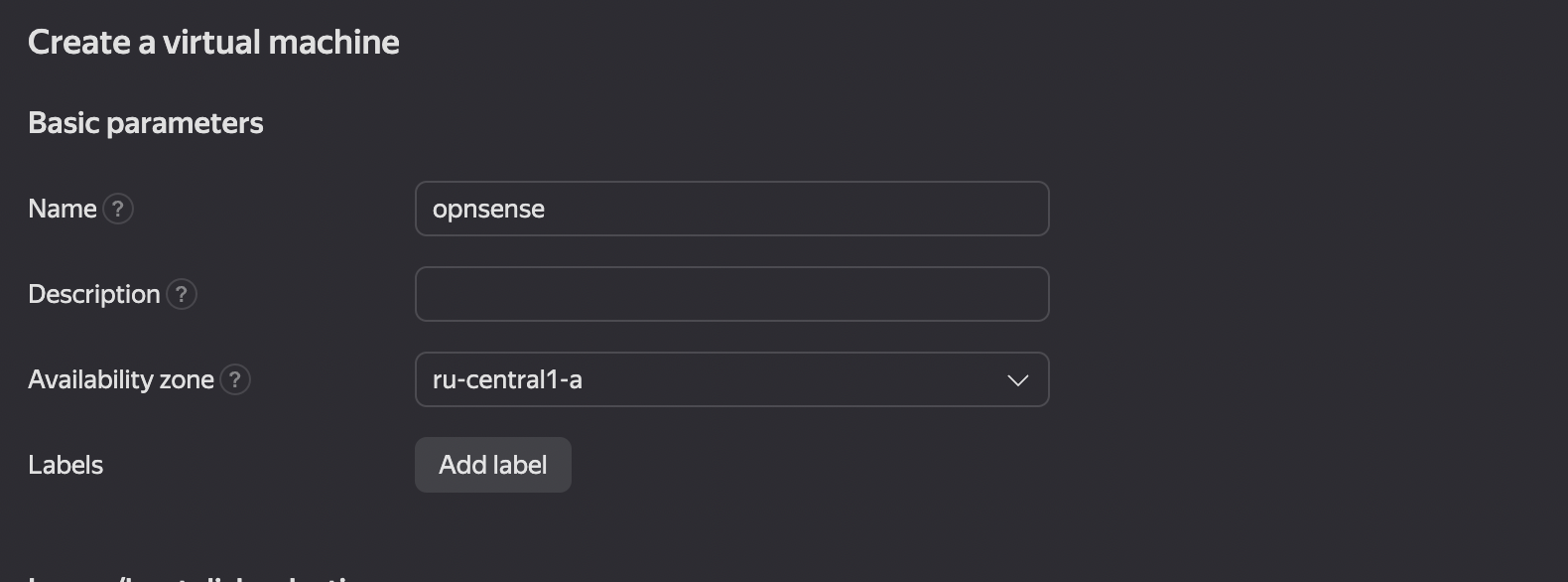
Figure 1. Creating a Virtual Machine in Yandex Cloud
- The user must specify the name of the virtual machine and define the Availability zone. Labels can be added if needed. Then, the user should select an OPNsense image from the Cloud Marketplace. (see Figure 2).
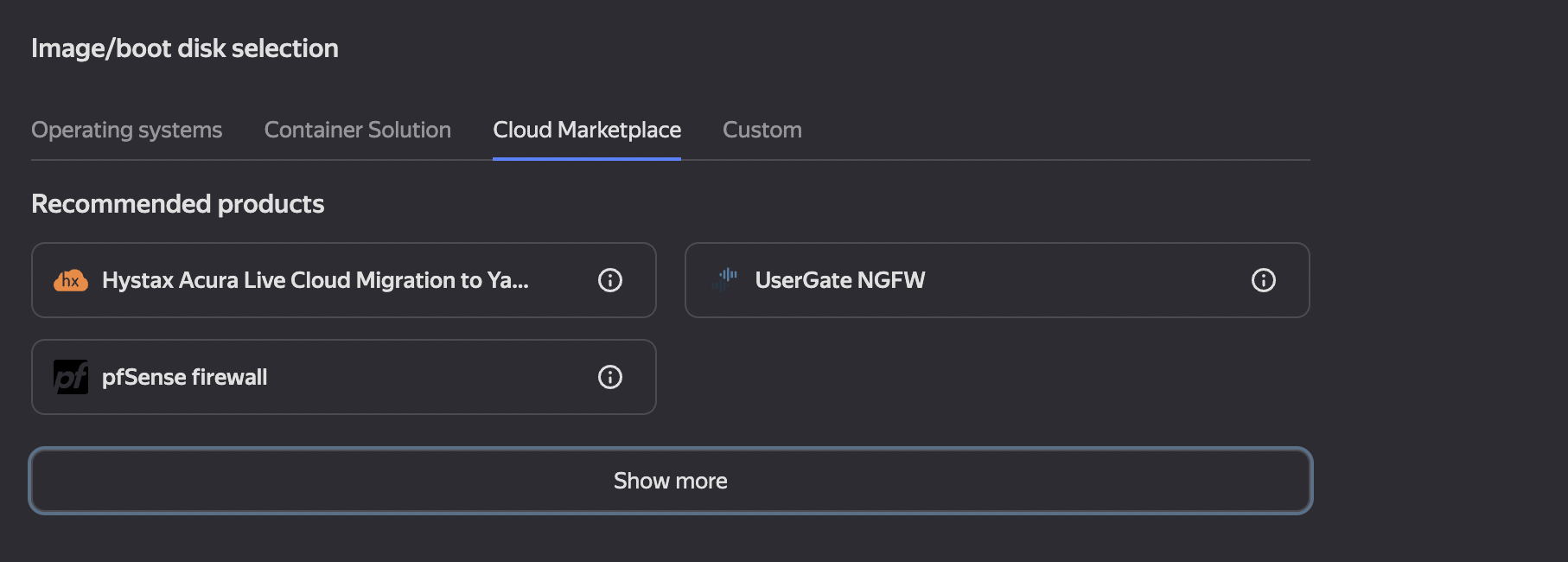
Figure 2. Selecting an Image From Cloud Marketplace
To display additional parameters, press “Show more”. Depending on the user’s settings, the menu items may differ.
Type the initial letters of the required package in the search line, for example, “opn” (see Figure 3).
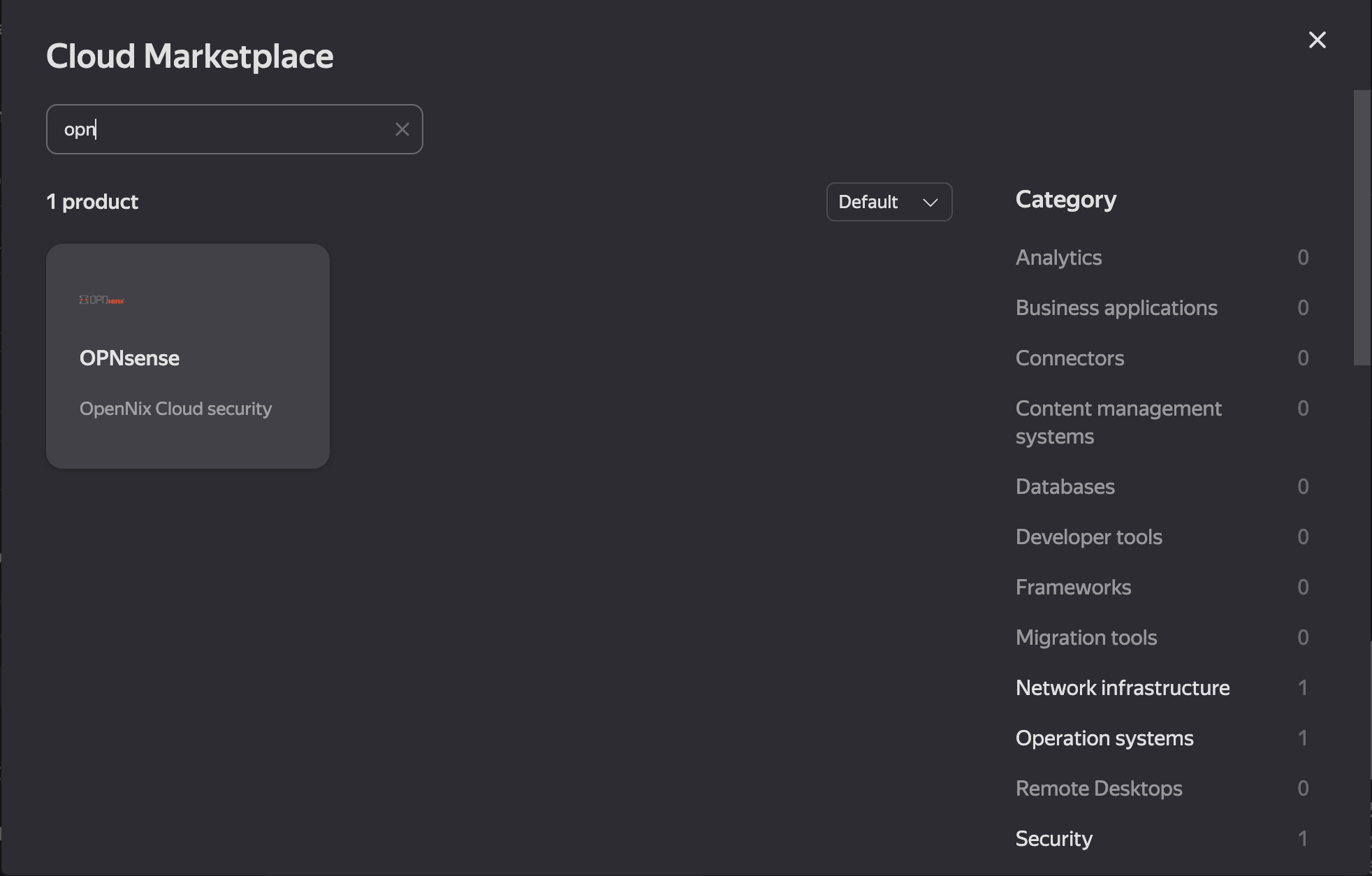
Figure 3. Search for the OPN Package in the Cloud Marketplace
After that, the user should select the corresponding item.
- The disk size can be set according to the user’s preferences or left at the default value (see Figure 4).
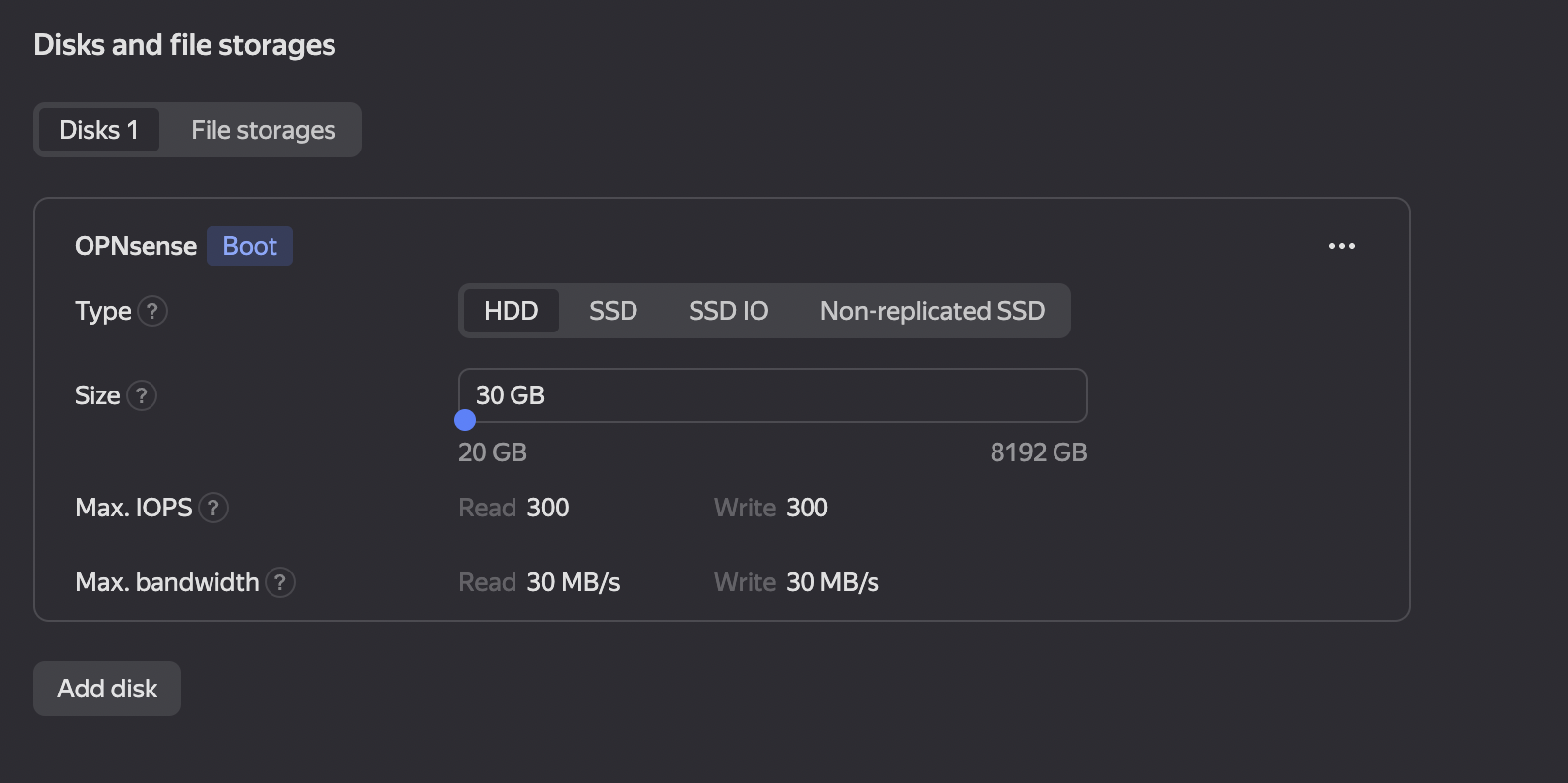
Figure 4. Setting up Disks and Storage
- The number of RAM and processor cores also depends on the user’s preferences and matches his specific tasks. The default values are used in our example (see Figure 5).
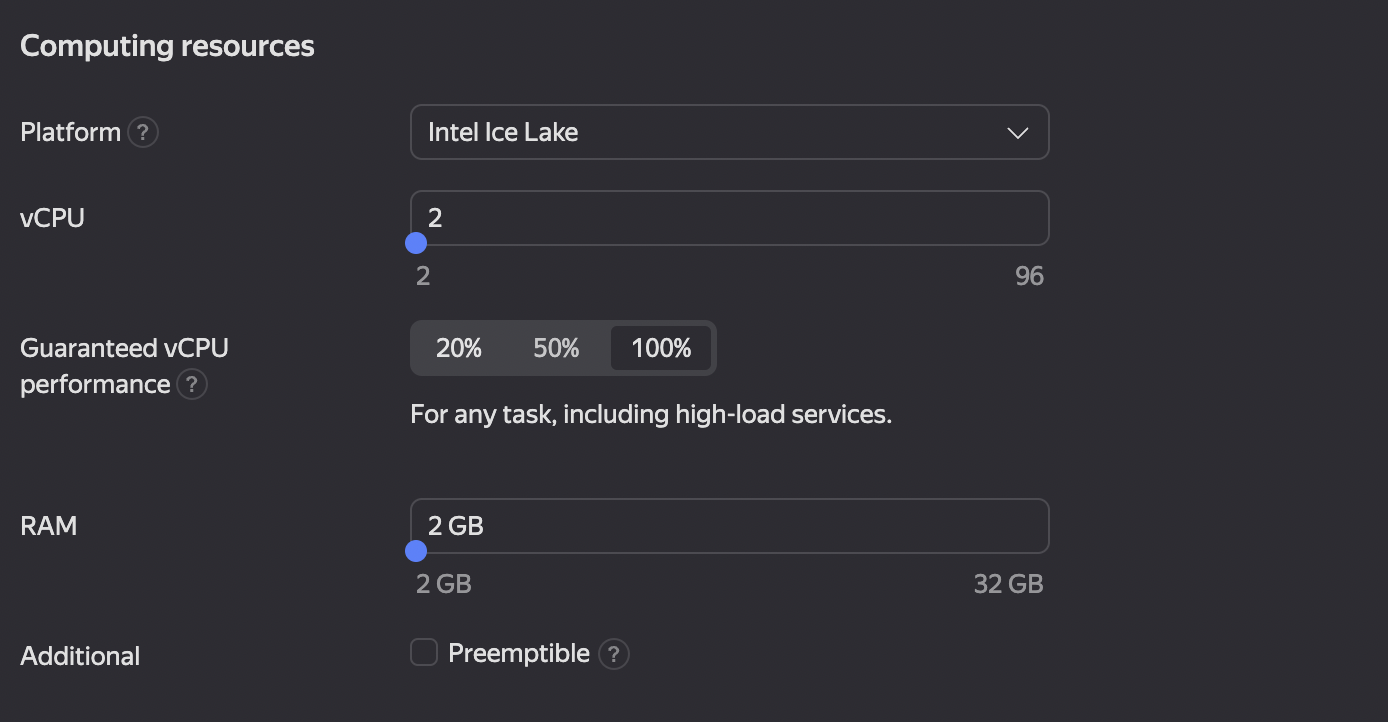
Figure 5. Configuring the RAM size and the number of vCPU
- The next step is to configure the network
Select the appropriate network for the WAN interface. The settings can be left unchanged, but it is crucial to ensure that the subnets do not overlap (see Figure 6).
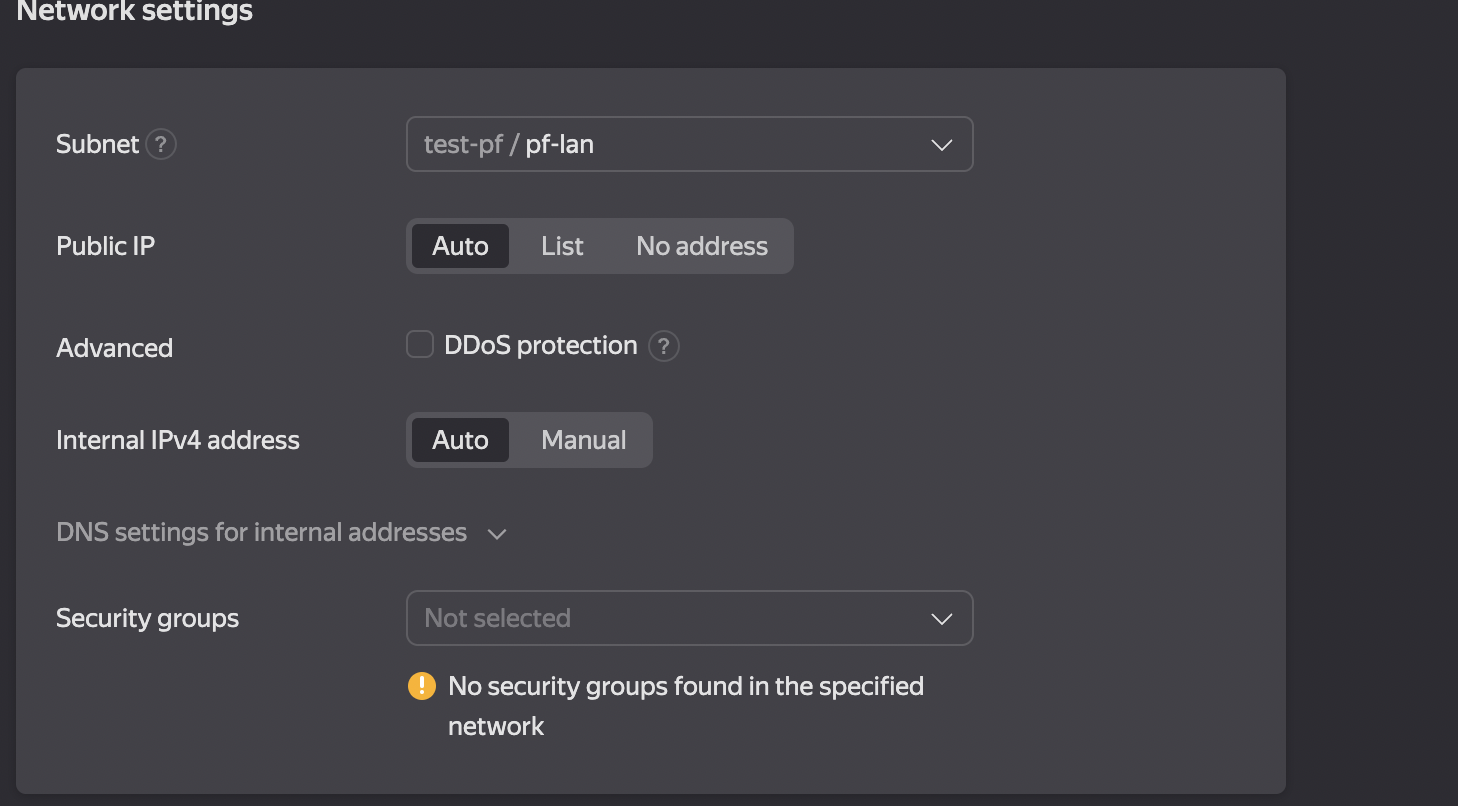
Figure 6. Settings a WAN Interface/p>
The next step is to add an additional LAN interface that will serve as a gateway for private networks (see Figure 7).
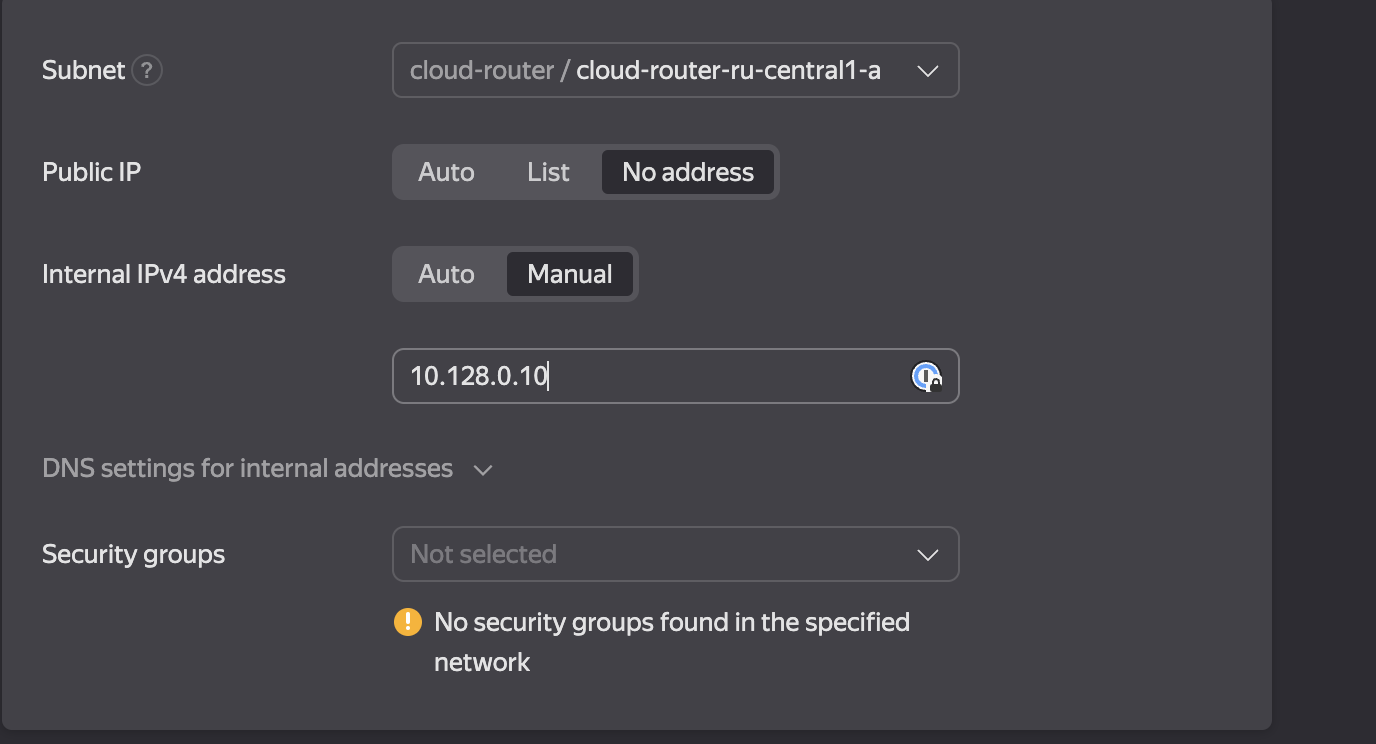
Figure 7. Settings a LAN Interface/p>
The LAN interface does not require a public IP address. We recommend using static IPv4.
At this point, the user can set a username for SSH and provide a public key. In this case, it is sufficient to specify the user “freebsd”.
Then the user needs to click on the “Create Virtual Machine” button. The VM creation process will take some time. After completing the creation of the virtual machine, the user will be able to connect to it via SSH.
Configuration complete.